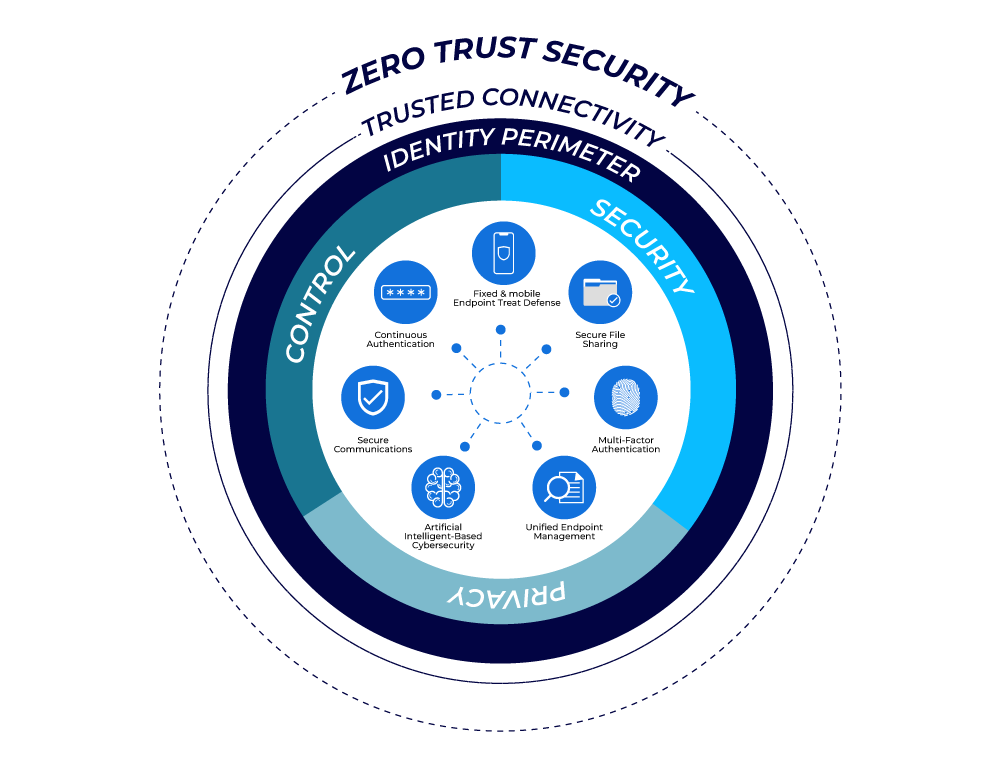
Zero-Trust Security
Zero-trust security: Zero-trust security is not just another cybersecurity buzzword. It is a mindset shift that reflects how modern organizations actually work today. Employees connect from home, coffee shops, airports, and mobile devices. Data lives in the cloud, not just behind office firewalls. In this environment, assuming that anything inside a network is safe is no longer realistic.
Zero-trust security works on one simple idea: trust nothing by default. Every user, every device, and every request must prove itself before access is granted. It does not matter if the request comes from inside the office or across the world. Verification is mandatory every time.
Think of zero-trust like airport security. You do not get checked once and then roam freely everywhere. Your identity, boarding pass, and sometimes even your behavior are checked at multiple points. That is exactly how zero-trust security treats digital access.
Why Old-School Cybersecurity Fails Today
Traditional cybersecurity models were built for a very different era. Most employees worked from a single office. Servers were on-site. Networks had clear boundaries. Firewalls acted like castle walls, keeping attackers out while trusting everyone inside.
Fast forward to today, and that castle has no walls. Cloud services, SaaS platforms, remote teams, and third-party vendors have blurred the perimeter. Attackers know this. They no longer try to break in loudly. Instead, they steal credentials, exploit weak access controls, and quietly move inside systems.
Once inside a traditional network, attackers often face little resistance. Zero-trust security fixes this flaw by removing blind trust and enforcing constant checks.
The Philosophy Behind Zero-Trust
Zero-trust security is based on realism, not fear. It assumes that breaches will happen sooner or later. Instead of pretending systems are always secure, it focuses on limiting damage and detecting problems early.
This philosophy encourages organizations to:
- Question every access request
- Monitor activity continuously
- Reduce exposure wherever possible
Rather than building higher walls, zero-trust builds smarter doors.
Core Principles That Define Zero-Trust Security
Zero-trust security rests on a few essential principles that guide all decisions.
Verify Explicitly
Every access request must be verified using multiple signals. These include user identity, device health, location, time of access, and behavior patterns. Passwords alone are no longer enough.
Least Privilege Access
Users should only access what they absolutely need, nothing more. In the event that an account is compromised, this reduces risk and stops attackers from acting freely.
Assume Breach
Zero trust assumes attackers may already be inside the system. Continuous monitoring and rapid response are critical to stopping threats before they spread.
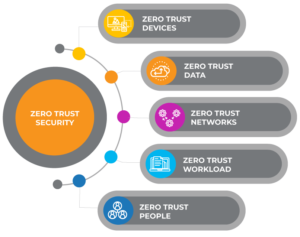
Key Building Blocks of a Zero-Trust Architecture
Zero-trust is not a single tool. It is a framework built from multiple security components working together.
Identity and Access Management
Strong identity controls ensure that users are who they claim to be. Multi-factor authentication, single sign-on, and adaptive access policies are essential.
Device Security and Compliance
Devices must meet security standards before accessing resources. This includes updates, encryption, and endpoint protection.
Network Micro-Segmentation
Instead of one large network, systems are divided into smaller segments. This limits lateral movement and isolates threats.
Continuous Monitoring and Analytics
Behavioral analytics and real-time monitoring help detect unusual activity quickly.
How Zero-Trust Security Actually Works
In a zero-trust environment, access is granted dynamically. When a user requests access, the system evaluates context in real time. If everything checks out, access is granted—but only to the specific resource requested.
If anything changes, such as a suspicious login location or a compromised device, access can be restricted instantly. This constant evaluation makes zero-trust flexible and resilient.
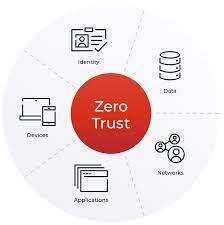
Zero-Trust vs Traditional Perimeter Security
Traditional security focuses on defending the network edge. Zero-trust focuses on protecting individual resources. The difference is significant.
Perimeter security assumes internal users are safe. Everyone must constantly demonstrate trust if there is zero trust. Because of this, zero-trust is far more effective against contemporary threats like ransomware, phishing, and insider threats.
Real-World Benefits of Zero-Trust Security
Organizations that adopt zero-trust security see measurable advantages.
Stronger Security
Breach containment improves, and attack surfaces decrease.
Better Visibility
Deep insights into user behavior and system health are provided by ongoing monitoring.
Support for Remote Work
Zero-trust enables secure access from anywhere without heavy reliance on VPNs.
Lower Breach Impact
Even if attackers gain access, damage is limited.
Challenges and Limitations of Zero-Trust
Zero-trust security requires planning and patience. Legacy systems may not integrate easily. Employees may initially resist stricter controls. Costs and complexity can also be concerns.
However, gradual implementation and clear communication help overcome these challenges.
Zero-Trust Security for Small and Growing Businesses
Zero-trust is not just for large enterprises. Small businesses face the same threats, often with fewer resources. Cloud-based zero-trust solutions make it affordable and scalable for smaller teams.
Zero-Trust in Cloud Computing and Remote Work
Cloud environments thrive on zero-trust principles. Access is identity-based rather than location-based. This makes zero trust ideal for hybrid and remote workforces.
Identity and Access Management in Zero-Trust
Identity is the foundation of zero-trust. Strong authentication, role-based access, and continuous validation ensure only authorized users gain access.
Data Protection and Zero-Trust Security
Zero-trust protects data at every stage. Encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention tools ensure sensitive information stays secure.
Compliance, Governance, and Zero-Trust
Zero-trust aligns well with regulatory requirements. Strong access controls, audit trails, and monitoring simplify compliance efforts.
A Brief Guide to Health Insurance Benefits in Secure Organizations
Security is not just about systems; it is also about people. Organizations that invest in strong cybersecurity often recognize the importance of employee well-being.
Health insurance benefits play a key role in maintaining a stable and focused workforce. Employees with access to reliable health coverage experience less stress and greater job satisfaction. This indirectly supports security by reducing burnout, human error, and risky behavior.
Comprehensive health insurance plans typically cover medical care, preventive services, and mental health support. When employees feel protected, they are more likely to follow security policies and contribute positively to organizational resilience.
Future of Zero-Trust Security
Zero-trust will continue to evolve. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation will enhance threat detection and response. Zero-trust principles will also expand into IoT and supply chain security.
Steps to Start Your Zero-Trust Journey
Organizations should begin with asset identification and risk assessment. Implementing strong identity controls, enforcing least privilege, and gradually introducing segmentation sets a strong foundation.
Common Myths About Zero-Trust Security
Many believe zero-trust is a one-time project. In reality, it is an ongoing strategy. Others think it slows productivity, but properly designed zero-trust systems often improve user experience.

Conclusion
Zero-trust security represents a realistic and forward-thinking approach to cybersecurity. By eliminating assumptions and enforcing continuous verification, organizations can protect their data, systems, and people more effectively.
Zero-trust contributes to the development of robust, safe, and human-centered organizations when paired with robust employee support programs like full health insurance benefits. Zero-trust is necessary in a world where boundaries have vanished and threats are ever-present.
FAQs
What is the true meaning of zero-trust security?
It means no user or device is trusted automatically. Every access request must be verified continuously.
Is zero-trust suitable for small businesses?
Yes, modern cloud tools make zero trust affordable and scalable for small organizations.
Does zero trust eliminate the need for VPNs?
In many cases, yes. Zero-trust reduces reliance on VPNs by securing access at the identity level.
How does zero trust help with compliance?
It enforces strict access controls, monitoring, and auditability required by many regulations.
Can zero trust improve employee productivity?
When implemented correctly, it provides secure and seamless access without unnecessary barriers.